

When compared to a sigma bond, a pi bond is less reactive. The charge symmetry of sigma bonds is cylindrical.Ī sigma bond has a high degree of reactivity. Alkynes, on the other hand, have one sigma bond and two pi bonds. Alkenes, for example, have one sigma bond and one pi bond. They only occur when a sigma bond is present. Alkanes, for example, have only one bond, the sigma bond. The pi link isn’t as strong as other bonds. Side-to-side overlapping of hybrid orbitals forms a pi bond (above and below the bonding axis). Head-on overlapping of hybrid orbitals forms a sigma bond (along the bonding axis). The pi bond has no bearing on the molecule’s form. The sigma bond determines the shape of the molecule.

One or more pi bonds are generated when two atoms contact. Only one sigma bond is generated when two atoms engage.
#PI BONDS VS SIGMA BONDS FREE#
The free rotation of orbitals is limited since the bond is established above and below the axis. The symbol 𝝿 is commonly used to represent it.īecause the bond is created along the axis, orbitals can freely rotate. Pi bond formation occurs in unsaturated compounds like alkenes and alkynes.
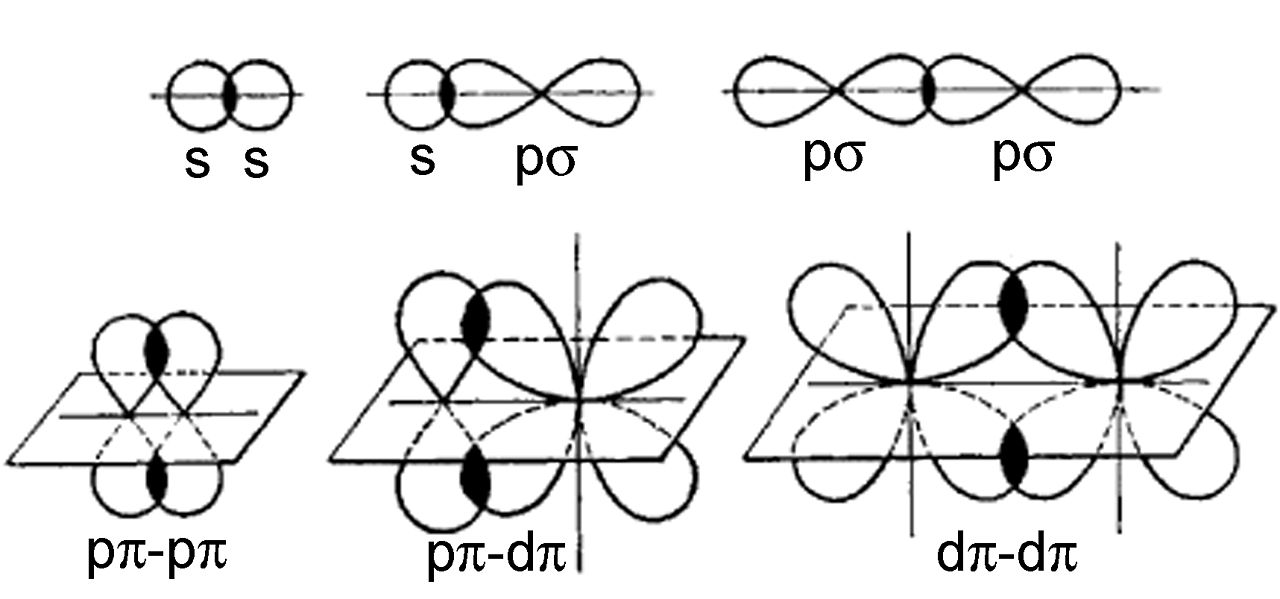
In molecular orbital theory, both are often employed to predict molecule behavior. Sigma bonds are generally stronger than pi bonds. This occurs in two ways, resulting in two types of covalent bonds: sigma and pi bonds. The way atomic orbitals overlap affects a variety of bond parameters, including bond length, bond angle, and bond enthalpy. The Greek letters sigma and pi are used to create both names. Sigma bonds are formed when two atomic orbitals overlap head-to-head, whereas pi bonds are formed when two atomic orbitals overlap laterally. Covalent bonds are formed when atomic orbitals overlap. Sigma and pi bonds are distinguished by the overlapping of atomic orbitals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
